Designing electronic circuit is only the beginning of translating an idea into a physical product. The next important step is to translate your schematic design into a layout on a PCB board. This is known as PCB circuit design. A PCB board provides the platform to hold electronic components (IC chip, resistors, capacitors, inductors, etc…) and enable their connection (known as PCB traces). It is also the main means to replicate the connections for mass production purpose. Most PCB boards are green in colour (we call it green coloured mask).
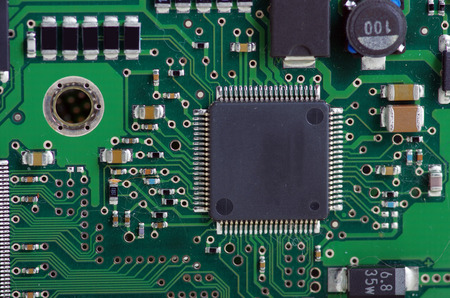
For small quantity production or simple electronic circuit prototype, PCB circuit design is usually not required. This is because designing the layout for the circuit can take up engineering effort. A typical simple circuit can take from 3 to 7 days to design and layout. This is a fixed cost prior to your production. Good news is that you only need to do it once. With this PCB blueprint (commonly refer to as Gerber files) you can reproduce as many PCB board as you like. For larger mass production quantity, the circuit design and layout cost is usually insignificant compare to the cost of each board. If you are only producing a few pieces of a simple electronic design for prototype testing purpose, this engineering effort may not be worth the value. It maybe cheaper to use a prototyping board instead to build and test your design.
PCB Design
The PCB circuit design is a combination of knowledge in electronic and user interface art. Engineering know-how to ensure the circuit works without issues, and also to design it in a simple manner such that the people using the circuit board product can easily handling it.
Engineering Know-How
Design PCB board requires a certain skill set. Besides the basic knowledge of electronic, a good foundation in the area of RF (Radio Frequency) is preferred. It may seem odd so some. What is RF going to do with PCB design? Wireless and PCB is a different topic, aren’t they? No. In fact, they are very much closely related. Knowledge of RF provides us with a strong understanding of how electronic circuit behaves under high-frequency condition. It is also related to how the electronic components and traces should be layout in order to keep the signal integrity within an acceptable tolerance, keeping the noise (unwanted signal) minimum. This is especially important when your electronic design contains sensitive analogue circuit, high-speed digital circuit or RF circuits. There rules to follow to ensure that the electronic signal maintains its integrity.
General rules that you can follow
- Learn to identify and categorises circuit trace. For example Power, Digital, Analog, RF traces.
- Design the PCB layout from left to right, starting from the power, input, and finally to the output.
- High power circuit modules, input or output should be located closely to one another to shorten the trace. This not only reduces board space it also minimise temperature rise.
- Power trace should be board enough to conduct the current without generating significant heat. As far as possible VCC & GND trace should be routed in a pair close to one another. This is to minimise the open (or known as loops) between the VCC & GND trace. The same applies to other types of traces. Power distribution is better to be in a star configuration. This is especially if the circuit module is very noise or high current. A delicate trace directly from the power source to the noisy circuit helps isolate it from the rest of the circuit.
- For digital data trace, if the data is of high-speed type, try to route it closely to a digital GND. Data rate >10Khz, you should start to consider proper digital trace routing.
- Analog signal trace, route it close to its GND trace as a pair. Leave sufficient gap away from high power or high-frequency digital trace.
- Group related circuit module tightly together to minimise the length and number of trace between circuit modules.
- Digital circuit and Analog circuit should have their own GND route. Should not mix.
- Before starting your 2 layer PCB board design, decide if the top or bottom layer should take on a horizontal or vertical trace. For example, if top layer traces are drawn horizontally, then the bottom trace should be vertical. This will help make tight routing simpler.
- For those un-used PCB board surface, use GND copper pour near circuit that generates more heat (for example, copper pour near power circuit). The copper pour acts as a heat sink for the heat. Also, you may like to copper pour over the area that contains sensitive analogue circuitry.
Design for Usability and Maintenance
- For side entry connector, if possible, consolidate them on one side so that the installation space needed for wiring can be minimised.
- A component with polarity +/- should have silkscreen indicating the component’s polarity. (Diode, LED, IC, Capacitor, etc…)
- If space permit, print the component value next to the component.
- Design surface mount component. It saves space and is easier to assemble compared to through hole components.
Quick PCB Design Checklist before sending for PCB fabrication
Here is a quick checklist to go through after you design the PCB board. This check list wraps up the additional details completing your PCB board design.
- Mounting hole for PCB board. (usually 3.2mm hole for M3 screw size)
- Ensure the input and output port connector is properly labelled for the user.
for example:- Pwr In, + 12V –
- LED indicator, RUN, COMM, ERROR
- Switch and Jumper pins.
- Input-Output Connector, Port01, Port02, +/-
- Ethernet, RS232, RS485
- Label for the name, product code and version for the PCB design.
for example:
USB I/O Controller
PIC-304 ver1.0
Made In Singapore - Labelling of components and its value on the PCB board to aid in the production.
- Setup some test pin or pad for production testing process, verifying for the valid voltage.
- check for power input voltage
- check for regulated voltage
- check for analogue circuit voltages
Typical PCB material specification
Before any PCB fabrication is started, you will need to specify the type of material to be used for your PCB. There are many types of material specification. For a typical industrial grade PCB material, it is recommended to use the commonly available,
Typical PCB specification: FR4, 1.6mm, 2L, 1oz copper, Green Mask, White Silk, HASL.
- FR4 is the fiberglass material PCB board. There are also other type of PCB board materials. Some cheaper cost, lower durability. Some are used for specific high frequency application, which can be more expensive. FR4 is the most commonly available material and good enough for most application.
- 1.6mm is a common PCB thickness. Most components, connectors (RJ45, DB9) footprint uses this standard thickness.
- 2L means 2 layer PCB board.
- 1oz copper is the thickness of the copper layer. 1oz is good enough for most application. If your trace is small and current flowing through is high, you may like to increase it to 2oz or more to minimise the heat that can be generated from the trace.
- Green Mask, the color of the mask which is also the PCB board color. Some of the commonly used color are blue, red, black, white, etc… Green mask is still the best, trace is more visible.
- White Silk, specify the color of the silkscreen printing use for all the components and connectors labeling.
- HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) specify the type of plating/costing to the exposed copper pad. Without the coating, it means that the expose surface will be bare copper. Leaving the copper surface expose to the air can result in oxidation on the surface. Once the pad is oxidation, soldering will become difficult. Even if it can be soldered, the soldered joint will not be good. This may cause intermediate issue when your circuit board is operating. There are many type of finishing. Gold plating is one of the options. A minimum plating thickness is required to minimise oxidation. Gold is expensive and is typically not needed. HASL is simply a coating of solder on the copper pad to prevent it from oxidation. It is a common cost effective method.
You can also check out more details of this recommended PCB specification on this page.
These are the basic things you should take note when designing your own electronic PCB circuit. If you need further assistance regarding PCB design or electronic circuit design, feel free to contact PIC-CONTROL using the message form on the right side bar of this page.